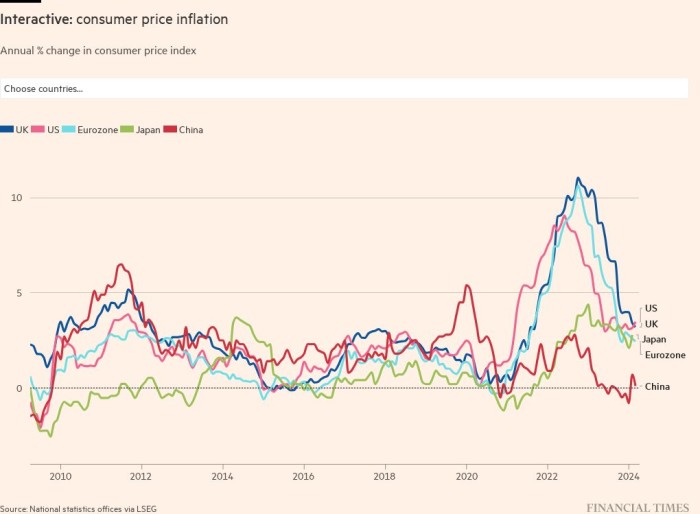
A lot of the world is experiencing a dramatic bout of inflation. But many central banks are holding rates of interest at or near file lows, regardless of the rise in costs brought on by greater vitality prices, sturdy client demand and the disruption to international provide chains wrought by coronavirus and its newest variants.
Some concern this mixture would possibly mark a normal return to the power inflation of the Nineteen Seventies. The one exception to the worldwide sample of rising costs are east Asian international locations comparable to China and Japan. However even right here, there are indicators that inflation is beginning to rise.
This web page offers a repeatedly up to date visible narrative of client worth inflation all over the world, each now and for subsequent yr.* It additionally separates inflation into its primary elements; what greater meals costs imply for customers; and the place buyers assume inflation is heading over the medium time period.
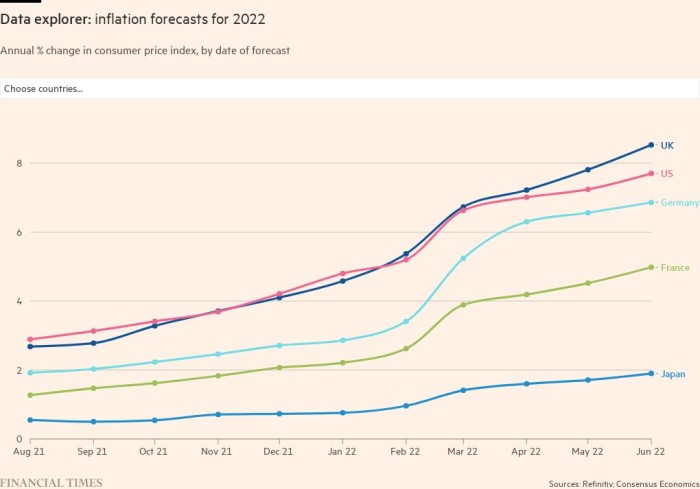
One of many details of debate amongst policymakers and economists is whether or not the rise in costs is transitory and can fade quickly, or whether or not it might show extra everlasting.
But even amongst those that imagine that inflation will fall subsequent yr as provide chain issues ease and client demand stabilises, there’s an acceptance that the inflationary shock will last more than first estimated. Economists polled by Consensus Economics, an organization that collates the predictions of main forecasters, have steadily revised up their anticipated inflation figures for 2022.
Rising inflation is a problem for central banks, not least these G7 international locations which have a worth stability goal of two per cent. To achieve that objective, central banks can regulate financial coverage to curb demand. However such instruments are much less efficient in tackling inflation created by lack of provide. Because the governor of the Financial institution of England, Andrew Bailey, has mentioned, financial coverage “doesn’t get extra gasoline, extra laptop chips, extra lorry drivers”.
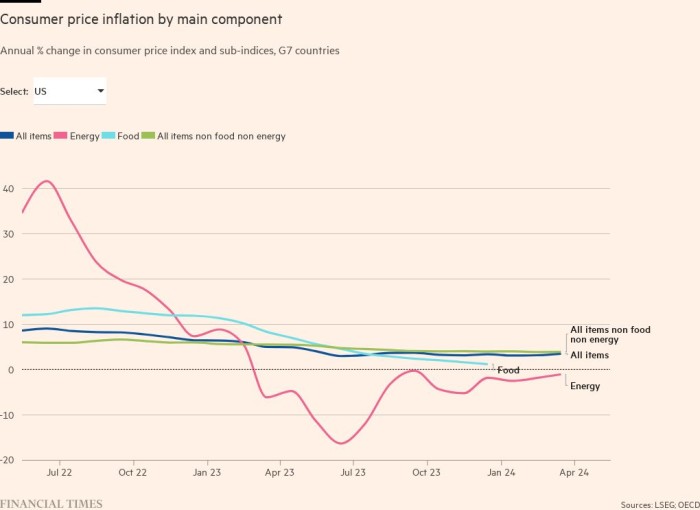
The rise in vitality costs, which has pushed inflation in lots of international locations, is a working example. In a single telling signal that inflation could also be beginning to unfold past vitality, the value of many different gadgets can be growing — particularly in international locations the place client demand is robust sufficient for companies to go on greater prices.
Rising costs restrict what households can spend on items and providers. For the much less properly off, that would result in them being unable to afford primary wants, comparable to meals and shelter.
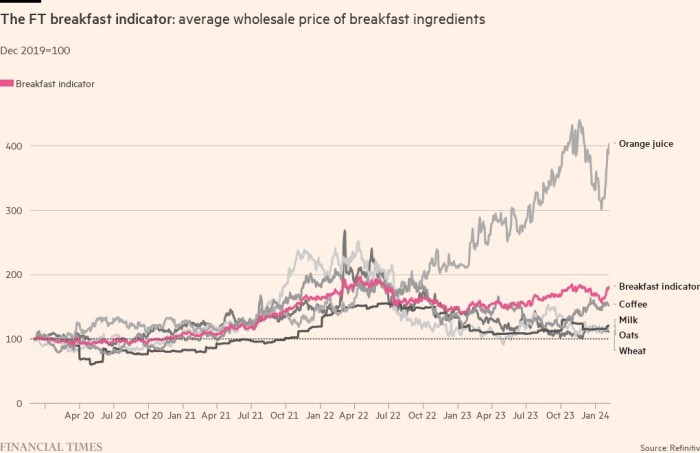
Every day knowledge on staple items, such because the wholesale worth of breakfast components, present an up-to-date indicator of the value pressures confronted by customers. In creating international locations, the wholesale value of those components has a bigger impression on closing meals costs; meals additionally accounts for a bigger share of family spending.
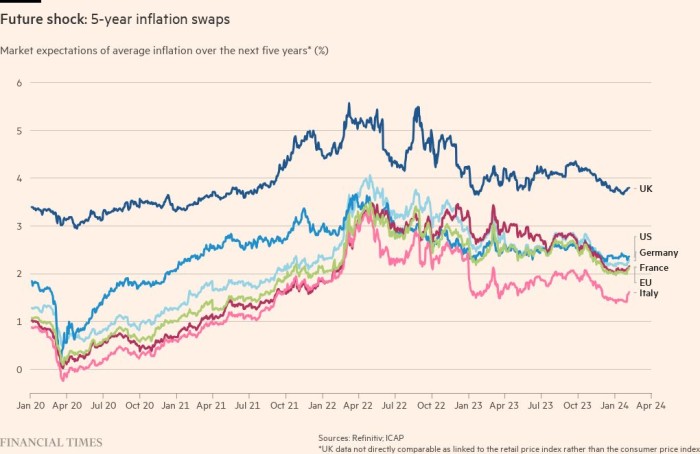
The talk over whether or not the surge in inflation is non permanent or extra everlasting continues. Supporters of “staff transitory” imagine this yr’s worth spikes are on account of a one-off surge in client demand bumping in opposition to a one-off rise in provide chain disruptions. Supporters of “staff everlasting” level to a broadening sample of worth rises, particularly in international locations the place a scarcity of employees is pushing up wages.
For now, markets appear to be siding with “staff everlasting” and, in lots of international locations, have steadily priced in an increase in inflation over the following 5 years.
*Shopper inflation refers to annual share adjustments in international locations’ client worth indices. This knowledge is internationally comparable, though some international locations and areas use a distinct headline determine. The eurozone, for instance, takes its harmonised client worth index as its headline determine, whereas additionally reporting the CPI